通过前面的分析,我们结束了对XML配置文件的解析,接下来将进行bean加载的分析。对于加载bean的功能,在Spring中的调用方式为:
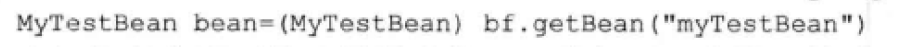
或者 MyTestBean tb = bf.getBean("myTestBean", MyTestBean.class);
一:整体分析
(1.1)AbstractBeanFactory 类
public abstract class AbstractBeanFactory extends FactoryBeanRegistrySupport implements ConfigurableBeanFactory { /** Parent bean factory, for bean inheritance support */ private BeanFactory parentBeanFactory; /** ClassLoader to resolve bean class names with, if necessary */ private ClassLoader beanClassLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader(); /** ClassLoader to temporarily resolve bean class names with, if necessary */ private ClassLoader tempClassLoader; /** Whether to cache bean metadata or rather reobtain it for every access */ private boolean cacheBeanMetadata = true; /** Resolution strategy for expressions in bean definition values */ private BeanExpressionResolver beanExpressionResolver; /** Spring ConversionService to use instead of PropertyEditors */ private ConversionService conversionService; /** Custom PropertyEditorRegistrars to apply to the beans of this factory */ private final Set<PropertyEditorRegistrar> propertyEditorRegistrars = new LinkedHashSet<PropertyEditorRegistrar>(4); /** Custom PropertyEditors to apply to the beans of this factory */ private final Map<Class<?>, Class<? extends PropertyEditor>> customEditors = new HashMap<Class<?>, Class<? extends PropertyEditor>>(4); /** A custom TypeConverter to use, overriding the default PropertyEditor mechanism */ private TypeConverter typeConverter; /** String resolvers to apply e.g. to annotation attribute values */ private final List<StringValueResolver> embeddedValueResolvers = new LinkedList<StringValueResolver>(); /** BeanPostProcessors to apply in createBean */ private final List<BeanPostProcessor> beanPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>(); /** Indicates whether any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors have been registered */ private boolean hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors; /** Indicates whether any DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors have been registered */ private boolean hasDestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors; /** Map from scope identifier String to corresponding Scope */ private final Map<String, Scope> scopes = new LinkedHashMap<String, Scope>(8); /** Security context used when running with a SecurityManager */ private SecurityContextProvider securityContextProvider; /** Map from bean name to merged RootBeanDefinition */ private final Map<String, RootBeanDefinition> mergedBeanDefinitions = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, RootBeanDefinition>(256); /** Names of beans that have already been created at least once */ private final Set<String> alreadyCreated = Collections.newSetFromMap(new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Boolean>(256)); /** Names of beans that are currently in creation */ private final ThreadLocal<Object> prototypesCurrentlyInCreation = new NamedThreadLocal<Object>("Prototype beans currently in creation"); /** * Create a new AbstractBeanFactory. */ public AbstractBeanFactory() { } /** * Create a new AbstractBeanFactory with the given parent. * @param parentBeanFactory parent bean factory, or {@code null} if none * @see #getBean */ public AbstractBeanFactory(BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) { this.parentBeanFactory = parentBeanFactory; } //--------------------------------------------------------------------- // Implementation of BeanFactory interface //--------------------------------------------------------------------- @Override public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException { return doGetBean(name, null, null, false); } @Override public <T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException { return doGetBean(name, requiredType, null, false); } @Override public Object getBean(String name, Object... args) throws BeansException { return doGetBean(name, null, args, false); } /** * Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean. * @param name the name of the bean to retrieve * @param requiredType the required type of the bean to retrieve * @param args arguments to use when creating a bean instance using explicit arguments * (only applied when creating a new instance as opposed to retrieving an existing one) * @return an instance of the bean * @throws BeansException if the bean could not be created */ public <T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType, Object... args) throws BeansException { return doGetBean(name, requiredType, args, false); } /** * Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean. * @param name the name of the bean to retrieve * @param requiredType the required type of the bean to retrieve * @param args arguments to use when creating a bean instance using explicit arguments * (only applied when creating a new instance as opposed to retrieving an existing one) * @param typeCheckOnly whether the instance is obtained for a type check, * not for actual use * @return an instance of the bean * @throws BeansException if the bean could not be created */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") protected <T> T doGetBean( final String name, final Class<T> requiredType, final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException { //提取对应的beanName final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name); Object bean; // Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons. Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName); if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) { logger.debug("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference"); } else { logger.debug("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'"); } } bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null); } else { // Fail if we're already creating this bean instance: // We're assumably within a circular reference. if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) { throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName); } // Check if bean definition exists in this factory. BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory(); if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) { // Not found -> check parent. String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name); if (args != null) { // Delegation to parent with explicit args. return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args); } else { // No args -> delegate to standard getBean method. return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType); } } if (!typeCheckOnly) { markBeanAsCreated(beanName); } try { final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName); checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args); // Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on. String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn(); if (dependsOn != null) { for (String dep : dependsOn) { if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'"); } registerDependentBean(dep, beanName); getBean(dep); } } // Create bean instance. if (mbd.isSingleton()) { sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() { @Override public Object getObject() throws BeansException { try { return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } catch (BeansException ex) { // Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there // eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution. // Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean. destroySingleton(beanName); throw ex; } } }); bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd); } else if (mbd.isPrototype()) { // It's a prototype -> create a new instance. Object prototypeInstance = null; try { beforePrototypeCreation(beanName); prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } finally { afterPrototypeCreation(beanName); } bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd); } else { String scopeName = mbd.getScope(); final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName); if (scope == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'"); } try { Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() { @Override public Object getObject() throws BeansException { beforePrototypeCreation(beanName); try { return createBean(beanName, mbd, args); } finally { afterPrototypeCreation(beanName); } } }); bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd); } catch (IllegalStateException ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " + "defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton", ex); } } } catch (BeansException ex) { cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName); throw ex; } } // Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance. if (requiredType != null && bean != null && !requiredType.isAssignableFrom(bean.getClass())) { try { return getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType); } catch (TypeMismatchException ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" + ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex); } throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass()); } } return (T) bean; } }
仅从代码量上就能看出bean的加载经历了一个相当复杂的过程,其中涉及各种各样的考虑。通过上面的代码,可以粗略了解整个Spring加载bean的过程。对应加载过程中所涉及的步骤大致如下:
(1)转换对应beanName
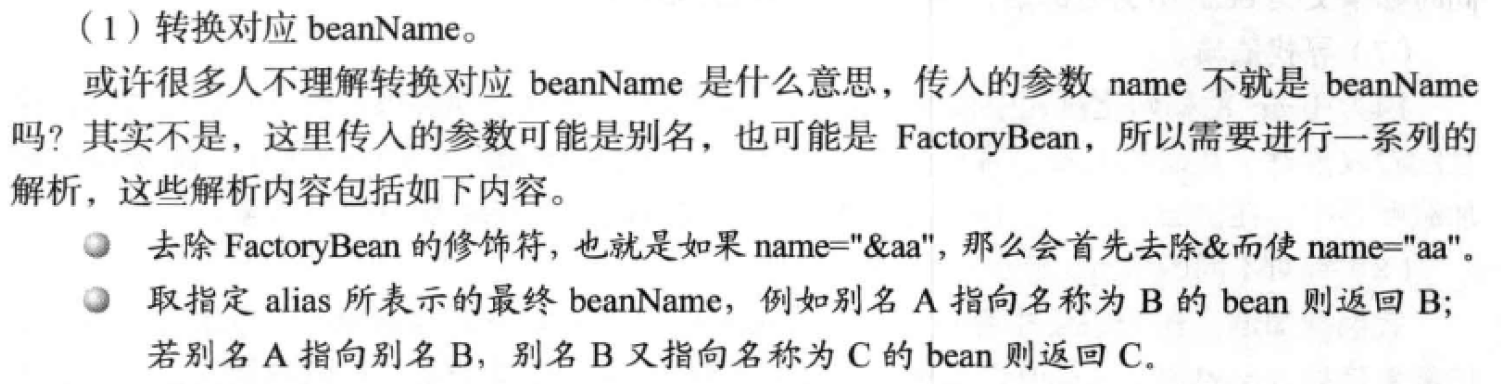
(2)尝试从缓存中加载单例。

(3)bean的实例化

(4)原型模式的依赖检查。

(5)检测parentBeanFactory

(6)将存储XML配置文件的GernericBeanDefinition转换为RootBeanDefinition

(7)剩下的步骤

经过上面的步骤,bean的加载就结束了,这个时候就可以返回我们所需要的bean了。其中最重要的就是步骤(8),针对不同的scope进行bean的创建,你会看到各种常用的Spring特性在这里的实现。
二:FactoryBean的使用
public interface FactoryBean<T> { /** * Return an instance (possibly shared or independent) of the object * managed by this factory. * <p>As with a {@link BeanFactory}, this allows support for both the * Singleton and Prototype design pattern. * <p>If this FactoryBean is not fully initialized yet at the time of * the call (for example because it is involved in a circular reference), * throw a corresponding {@link FactoryBeanNotInitializedException}. * <p>As of Spring 2.0, FactoryBeans are allowed to return {@code null} * objects. The factory will consider this as normal value to be used; it * will not throw a FactoryBeanNotInitializedException in this case anymore. * FactoryBean implementations are encouraged to throw * FactoryBeanNotInitializedException themselves now, as appropriate. * @return an instance of the bean (can be {@code null}) * @throws Exception in case of creation errors * @see FactoryBeanNotInitializedException */ T getObject() throws Exception; /** * Return the type of object that this FactoryBean creates, * or {@code null} if not known in advance. * <p>This allows one to check for specific types of beans without * instantiating objects, for example on autowiring. * <p>In the case of implementations that are creating a singleton object, * this method should try to avoid singleton creation as far as possible; * it should rather estimate the type in advance. * For prototypes, returning a meaningful type here is advisable too. * <p>This method can be called <i>before</i> this FactoryBean has * been fully initialized. It must not rely on state created during * initialization; of course, it can still use such state if available. * <p><b>NOTE:</b> Autowiring will simply ignore FactoryBeans that return * {@code null} here. Therefore it is highly recommended to implement * this method properly, using the current state of the FactoryBean. * @return the type of object that this FactoryBean creates, * or {@code null} if not known at the time of the call * @see ListableBeanFactory#getBeansOfType */ Class<?> getObjectType(); /** * Is the object managed by this factory a singleton? That is, * will {@link #getObject()} always return the same object * (a reference that can be cached)? * <p><b>NOTE:</b> If a FactoryBean indicates to hold a singleton object, * the object returned from {@code getObject()} might get cached * by the owning BeanFactory. Hence, do not return {@code true} * unless the FactoryBean always exposes the same reference. * <p>The singleton status of the FactoryBean itself will generally * be provided by the owning BeanFactory; usually, it has to be * defined as singleton there. * <p><b>NOTE:</b> This method returning {@code false} does not * necessarily indicate that returned objects are independent instances. * An implementation of the extended {@link SmartFactoryBean} interface * may explicitly indicate independent instances through its * {@link SmartFactoryBean#isPrototype()} method. Plain {@link FactoryBean} * implementations which do not implement this extended interface are * simply assumed to always return independent instances if the * {@code isSingleton()} implementation returns {@code false}. * @return whether the exposed object is a singleton * @see #getObject() * @see SmartFactoryBean#isPrototype() */ boolean isSingleton(); }
一般情况下,Spring通过反射机制利用bean的class属性指定实现类来实例化bean。在某些情况下,实例化bean过程比较复杂,如果按照传统的方式,则需要在<bean>中提供大量的配置信息,配置方式的灵活性是受限的,这时采用编码的方式可能会得到一个简单的方案。Spring为此提供了一个org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean的工厂类接口,用户可以通过实现该接口定制实例化bean的逻辑。


