| 项目 | 内容 |
|---|---|
| 课程 | 软件工程 |
| 作业 | 个人项目作业 |
| 教学班级 | 005 |
| GitHub地址 | https://github.com/yankuai/Interset.git |
PSP 表格
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | ||
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 10 | 10 |
| Development | 开发 | ||
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 60 | 120 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 40 | 40 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) | 40 | 20 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 20 | 20 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 60 | 180 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 180 | 180 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 90 | 60 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 120 | 180 |
| Reporting | 报告 | ||
| · Test Report | · 测试报告 | 30 | 30 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 10 | 10 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 30 | 30 |
| 合计 | 690 | 910 |
解题思路描述
总体思路
封装point,line和circle类。其中point类可以继承自STL pair<double,double>,line和circle类的属性应该体现其表达式的参数。
line一般式: (ax+by+c=0)
circle公式:((x-x_0)^2+(y-y_0)^2=r^2)
暴力算法寻找交点,计算每两个图形的交点,将交点放进STL set
直线与直线的交点
直线的一般表示:
(f(x) : ax + by + c = 0)
已知直线上两点((x_0,y_0),(x_1,y_1)),可以得到一般式的参数:
(a = y_0 – y_1)
(b = x_1 – x_0)
(c = x_0*y_1 – x_1*y_0)
以上两点坐标向直线一般式的转换在数据输入阶段完成。遍历直线计算交点时,由一般式计算直线交点的方程为:
(x = (b_0*c_1 – b_1*c_0)/D)
(y = (a_1*c_0 – a_0*c_1)/D)
(D = a_0*b_1 – a_1*b_0)
使用一般式的好处是,不需要单独考虑斜率为0的情况。
圆与圆的交点
回顾一下圆的两种表示方法:
圆的标准方程:((x−x_0)^2+(y−y_0)^2=r^2)
圆的参数方程:
将第一个圆的参数方程带入第二个圆的标准方程:
((x_1+r_1 cosθ−x_2)^2+(y_1+r_1 sinθ−y-2)^2=r_2^2)
展开后得到:
(2 r_1(x_1−x_2)cosθ+2 r_1(y_1−y_2)sinθ=r_2^2−r_1^2−(x_1−x_2)^2−(y_1−y_2)^2)
令:
(a=2r_1(x_1−x_2))
(b=2r_1(y_1−y_2))
(c=r_2^2−r_1^2−(x_1−x_2)^2−(y_1−y_2)^2)
原式变为:
(acosθ+bsinθ=c)
令(cosθ=x,sinθ=sqrt{1−x^2}) ,关于sin**θsinθ 的正负后面再判断。
代入方程,得到,(ax+bsqrt{1−x^2}=c)
移项再两边平方,((ax−c)^2=b^2(1−x^2))
整理得,((a^2+b^2)x^2−2acx+c^2−b^2=0),解一元二次方程得到(x,sinθ,cosθ)。
将(sinθ)和(cosθ)代回到第一个圆的参数方程,得到交点的坐标。
接下来需要注意,将求得交点带入第二个圆的方程验证,如果不在第二个圆上,说明(sinθ)是负数,需要对交点做调整。另一种特殊情况是,如果确定两个不同交点,解出来的(cosθ)只有一个,说明对应的(sinθ)值一正一负。
参考博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/AOQNRMGYXLMV/p/5098304.html
直线与圆的交点
求交点步骤如下
-
首先求出圆心c在直线l 上的投影点pr的坐标
-
计算向量p1p2的单位向量e, 再求出base的长度, 进而求出向量base
-
最后,以pr作为起点, 向正or负方向加上该向量, 就可以得到圆与直线的交点了
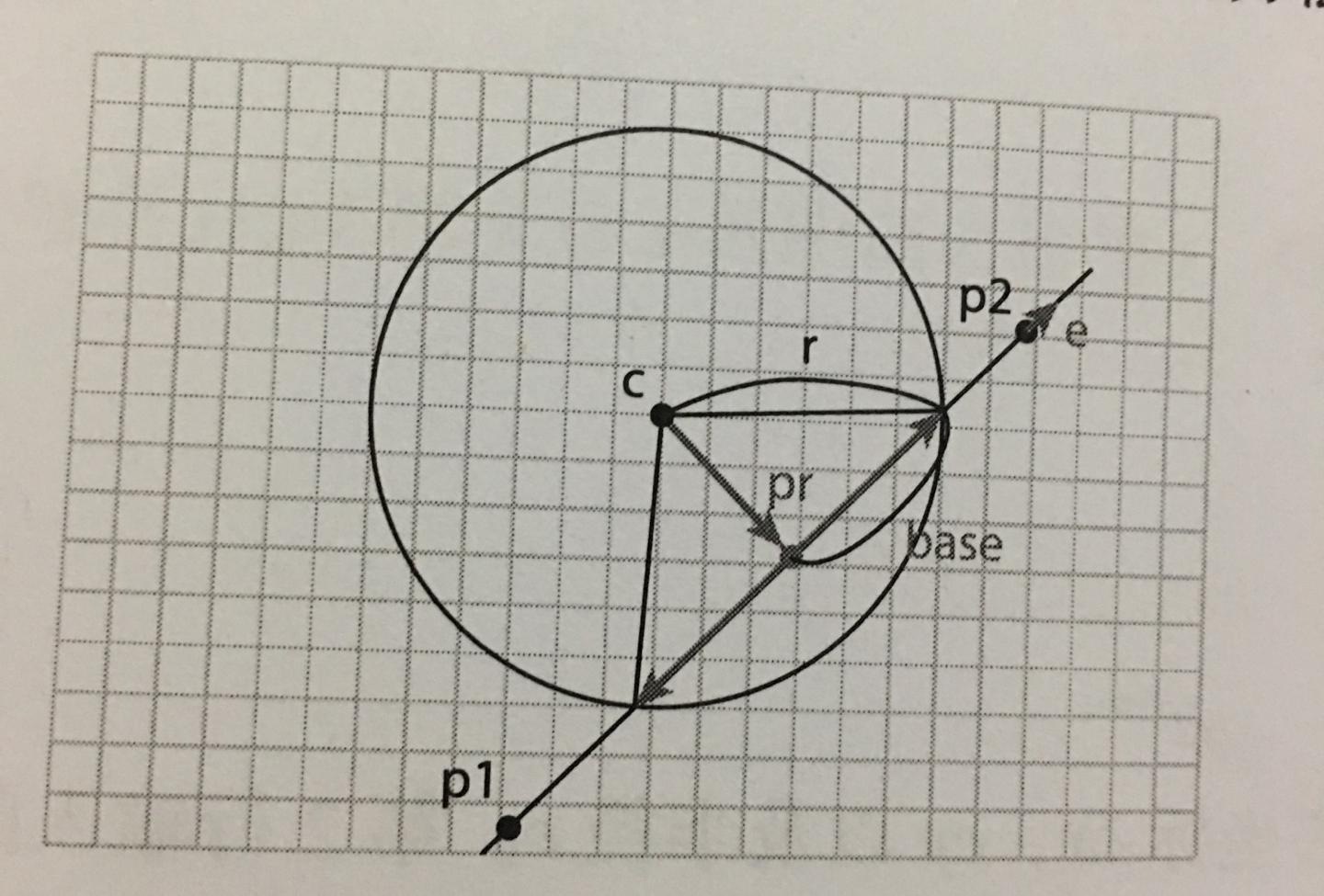
参考博客:http://www.pianshen.com/article/6764257/
设计实现过程
代码组织(几个类,几个函数,关系,关键函数流程图,单元测试设计)
代码组织
Point类
point不仅代表点坐标,还可以表示向量。在计算直线和圆的交点时,我运用了很多向量运算求圆心到直线的投影等,所以重写了operator方法,方便向量运算。
class Point : public pair<double, double> {
public:
Point() {}
Point(double x, double y);
Point operator - (const Point& p);
bool operator ==(const Point& p);
void operator=(const Point& point);
Point operator/(const double& d);
};
Line类
a,b,c是直线一般式的参数,e是直线的单位向量,p1,p2是确定直线的两点。
getIntersection_ll是求两直线交点的方法,传入set的指针,方法内直接将交点加入。
class Line {
public:
double a;
double b;
double c;
Point e;
Point p1;
Point p2;
Line() {}
Line(Point source, Point target);
void operator=(const Line& line);
int getIntersection_ll(set<Point>* intersections, Line l1, Line l2);
};
Circle类
getIntersection_cc是求两圆交点的方法。
class Circle {
public:
Point c;
double r;
Circle() {}
Circle(Point c, double r) :c(c), r(r) {}
void operator=(const Circle& circle);
int getIntersection_cc(set<Point>* intersections, Circle c1, Circle c2);
};
getIntersection_cl函数
求直线与圆交点的方法,不在line和circle类之中。其实把求两直线和两圆交点的方法分别放进line和circle类有些多此一举,因为参数还是会传入两个被观察的几何体,这两个方法类似于类中的静态方法,不用创建实例也可以用。
Geometry结构体
包含图形的标签(圆,直线),和图形自身的类。是为了实现将line和circle类存入一个vector容器,这样在遍历图形的时候更方便。
enum GType { L, C };
struct Geometry {
GType Gflag;
union {
Line lObj;
Circle cObj;
};
Geometry(Line l) {
Gflag = L;
lObj = l;
}
Geometry(Circle c) {
Gflag = C;
cObj = c;
}
void getObj(Line& obj) {
if (Gflag == L) {
obj = lObj;
}
}
void getObj(Circle& obj) {
if (Gflag == C) {
obj = cObj;
}
}
};
参考博客:https://zouzhongliang.com/index.php/2019/06/22/stlrongqizhongcunfangbutongleixingshixianfangfa/
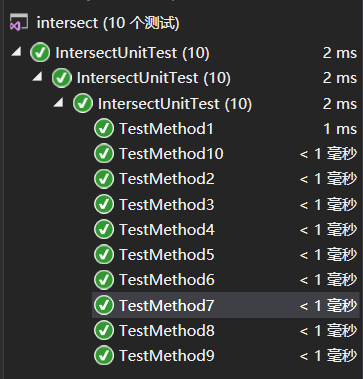
单元测试设计
单元测试考虑了十种情况,包括直线与直线相交(相交、平行、斜率不存在),圆与圆相交(相离、内含、相切、相交),圆与直线相交(相离、相切、相交)。在这些情况下均能通过测试。
性能改进思路
性能分析图
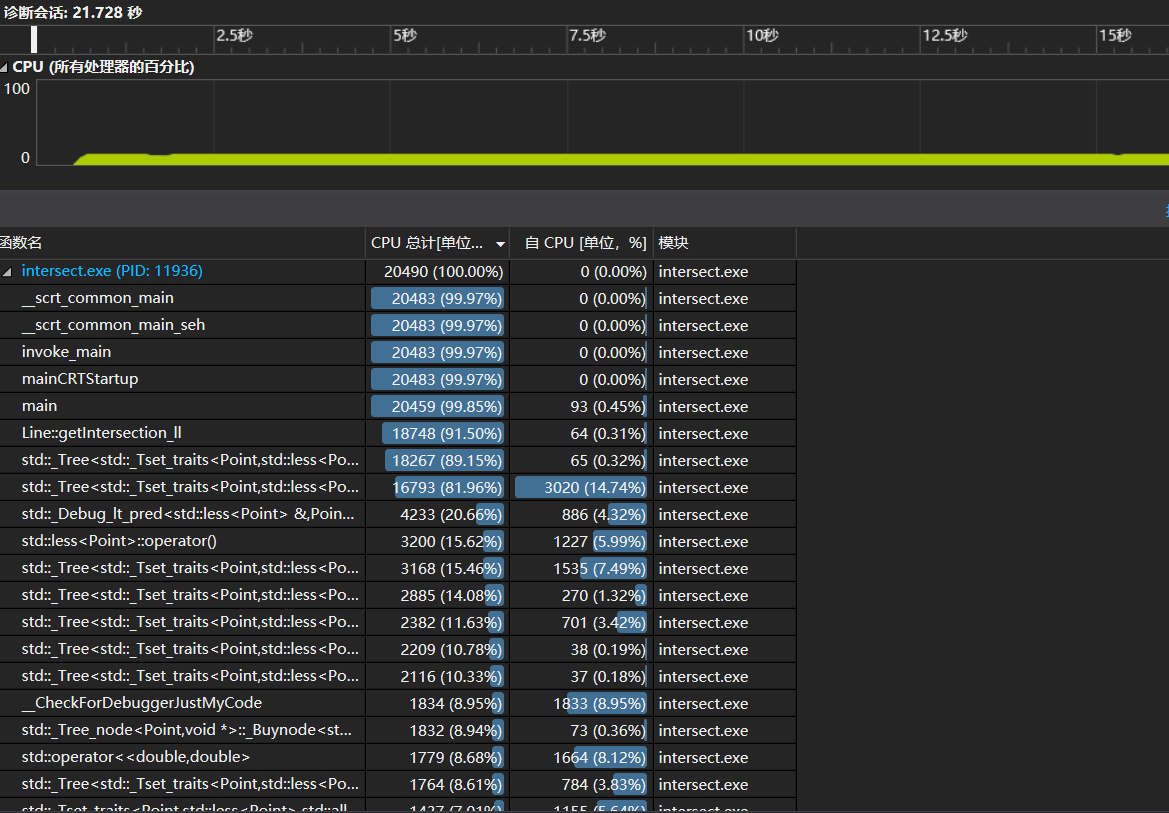
消耗最大的函数

将近90%时间都花在set的insert函数,其中两个点的比较运算最耗时。
改进思路
set的实现原理是红黑树,很难进一步优化。所以我尽量减少放进set的交点数,比如圆相切时,只把交点放进set一次。
代码说明
直线与直线交点
int Line::getIntersection_ll(set<Point>* intersections, Line l1, Line l2) {
double D = l1.a * l2.b - l2.a * l1.b;
if (D == 0) return 0;
Point p = { (l1.b * l2.c - l2.b * l1.c) / D, (l2.a * l1.c - l1.a * l2.c) / D };
p.first = (float)p.first;
p.second = (float)p.second;
intersections->insert(p);
return 1;
}
圆与圆交点
int Circle::getIntersection_cc(set<Point>* intersections, Circle c1, Circle c2) {
double r1 = c1.r, r2 = c2.r;
double x1 = c1.c.first, x2 = c2.c.first, y1 = c1.c.second, y2 = c2.c.second;
double d = length(c1.c - c2.c); //dist of circle center
if (dcmp(fabs(r1 - r2) - d) > 0) return -1;
if (dcmp(r1 + r2 - d) < 0) return 0;
double d2 = sqr(d); //d*d
double a = 2 * r1 * (x1 - x2);
double b = 2 * r1 * (y1 - y2);
double c = r2 * r2 - r1 * r1 - d * d;
double p = a * a + b * b;
double q = -2 * a * c;
double r = c * c - b * b;
double cosa, sina, cosb, sinb;
//one intersection
if (dcmp(d - (r1 + r2)) == 0 || dcmp(d - fabs(r1 - r2)) == 0) {
cosa = -q / p / 2; //被除数 p = a2 + b2 > 0
sina = sqrt(1 - sqr(cosa));
Point p(x1 + c1.r * cosa, y1 + c1.r * sina);
if (!onCircle(p, c2)) p.second = y1 - c1.r * sina;
p.first = (float)p.first;
p.second = (float)p.second;
intersections->insert(p);
return 1;
}
//two intersections
double delta = sqrt(q * q - 4 * p * r);
cosa = (delta - q) / p / 2;
cosb = (-delta - q) / p / 2;
sina = sqrt(1 - sqr(cosa));
sinb = sqrt(1 - sqr(cosb));
Point p1(x1 + c1.r * cosa, y1 + c1.r * sina);
Point p2(x1 + c1.r * cosb, y1 + c1.r * sinb);
if (!onCircle(p1, c2)) p1.second = y1 - c1.r * sina;
if (!onCircle(p2, c2)) p2.second = y1 - c1.r * sinb;
if (p1 == p2) p1.second = y1 - c1.r * sina;
p1.first = (float)p1.first;
p1.second = (float)p1.second;
p2.first = (float)p2.first;
p2.second = (float)p2.second;
intersections->insert(p1);
intersections->insert(p2);
return 2;
}
直线与圆交点
int getIntersection_cl(set<Point>* intersections, Circle c, Line l) {
if (dcmp(disLine(c.c, l) - c.r) == 0) { return 0; }
Point Base = vbase(c, l);
Point pr = prxy(c, l);
Point inter1 = { Base.first + pr.first, Base.second + pr.second };
Point inter2 = { pr.first - Base.first, pr.second - Base.second };
inter1.first = (float)inter1.first;
inter1.second = (float)inter1.second;
inter2.first = (float)inter2.first;
inter2.second = (float)inter2.second;
if (inter1 == inter2) {
intersections->insert(inter1);
return 1;
}
else {
intersections->insert(inter1);
intersections->insert(inter2);
return 2;
}
}
double disLine(Point p, Line l) { //点到直线距离
double a = l.a, b = l.b, c = l.c;
double x = p.first, y = p.second;
return fabs(a * x + b * y + c) / sqrt(a * a + b * b); //a,b不同时为0
}
Point vbase(Circle c, Line l) { //向量base
double r = c.r;
double base = sqrt(r * r - sqr(disLine(c.c, l)));
return Point(l.e.first * base, l.e.second * base);
}
Point prxy(Circle c, Line l) { //投影点pr的坐标
Point A = l.p1;
Point B = l.p2;
Point O = c.c;
Point AB = B - A;
Point AO = O - A;
double L = dot(AB, AO) / length(AB);
Point Apr(l.e.first * L, l.e.second * L);
return Point(A.first + Apr.first, A.second + Apr.second);
}
精度问题
可以发现,在进行交点比较的时候,使用了dcmp函数,而不是直接比较。dcmp允许比较数有些许误差,还是能返回相等的结果。造成大量的除法和开方运算造成了精度损失,使相同的交点坐标出现很小的差别。
int dcmp(double x) {
if (fabs(x) < eps) return 0;
return x < 0 ? -1 : 1;
}
另外在把交点加入set的时候,将double类型的坐标转换成float以降低精度,避免有细微差别的交点在集合里被当成两个不同的点。
我认为精度问题体现在两个地方,其一在计算交点坐标的时候,难免会有精度损失;其二在把交点放入集合的时候,比较交点时的比较精度会更高。是计算的低精度和比较的高精度造成的不适配,导致相同交点会在集合里出现两次。
- 方法一是提高计算精度,举例:
尽量把3.0计算成3.0000000000001而不是3.00001,这样在double省略掉后面位数时不会产生大误差。
- 方法二是降低比较精度,这里包括判断交点是否相等的显示比较(dcmp函数),以及set内部去重的隐式比较。对于降低set内的比较精度,可以在数据加入set前用强制类型转换降低数据的精度,或者不改变数据而重写set比较函数。举例:
如果计算精度没有提升,已经把3.0算成3.00001,那比较时只看小数点后4位,3.00001就还是3.0。
这两个例子的精确度只为做示范,实际比较函数要估算到小数点后几位,是很值得研究的问题,我还没有找到答案(肯定不是例子的位数啦)。亲测在我选用不同精确度,计算上千条直线交点时,有不同的结果。
代码分析截图